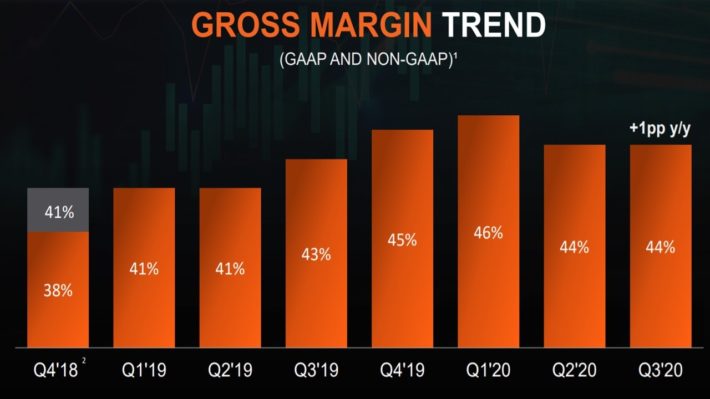Published on November 20th, 2020 by Aristofanis Papadatos
Advanced Micro Devices (AMD) is a high-growth tech stock, with impressive business momentum and exciting growth prospects ahead. The stock was trading below $2.00 in early 2016 but since then it has rallied to $85, thus rewarding its shareholders with life-changing returns.
The growth of AMD has accelerated this year thanks to the coronavirus crisis, which has forced people to work from home and stay at home more than ever, thus increasing the need for computers and gaming devices. This is clearly reflected in the stock price, which has more than doubled in the last 12 months.
With a market cap now above $100 billion, Advanced Micro Devices is a large-cap stock.
You can download your free copy of the large-cap stocks list, along with relevant financial metrics like price-to-earnings ratios, dividend yields, and payout ratios, by clicking on the link below:
Income investors may have missed the exceptional returns of AMD, as the company does not pay a dividend. This is fairly common among growth stocks, particularly those in the technology sector, as it is much more profitable to reinvest the earnings in the business than to distribute them to the shareholders. Of the 500 stocks that comprise the S&P 500 Index, nearly 90 do not pay a dividend to their shareholders.
Income-oriented investors who are attracted by the extraordinary returns of AMD may wonder if the company will pay a dividend anytime soon. While the initiation of a dividend cannot be excluded at some point in the future, AMD is not likely to initiate a dividend for many more years.
Business Overview
AMD operates as a semiconductor company worldwide. Its products include x86 microprocessors as an accelerated processing unit (APU), chipsets and graphics processing units (GPUs). The major segment of AMD is the Computing and Graphics, which generates approximately two-thirds of the revenues of the company.
AMD currently has the strongest notebook processor portfolio in its history. More than 105 AMD-based notebooks have come to the market this year, as the company has expanded its presence in divisions like gaming, commercial and education, in which it has traditionally been a minor player.
In late October, AMD reported its results for the third quarter of 2020. Its business performance accelerated in the quarter, as revenue jumped 56% over the prior year’s quarter, to an all-time high level, and earnings per share more than doubled thanks to the strong demand for Ryzen, EPYC and Semi-Custom processors.
Revenue in the primary segment, Computing and Graphics, grew 45% over last year’s quarter, primarily thanks to strong Ryzen processor sales, which more than offset a dip in graphic sales. The company achieved its highest client processor revenue in more than 12 years and posted nearly all-time high notebook processor unit shipments.
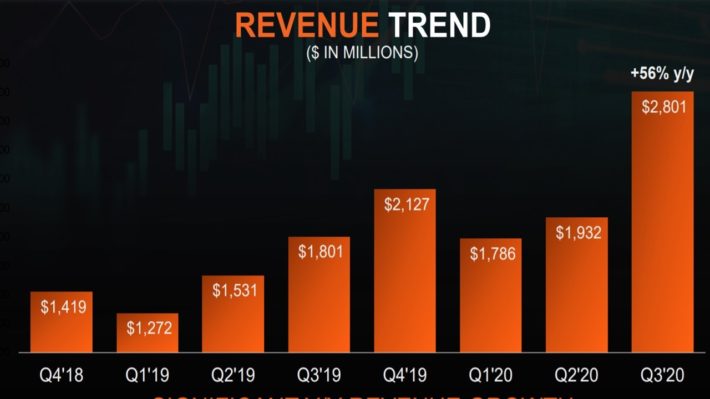
The strong business momentum of AMD is clearly reflected in the revenue trend.
Source: Investor Presentation
As shown in the above chart, revenue has temporarily stalled in some quarters but only due to seasonal issues related to the launch of new products.
AMD has also maintained strong gross margins for several quarters in a row.
Source: Investor Presentation
The strong margins result primarily from the dominant position of AMD in its business, as the company essentially operates in a duopoly, with Intel (INTC) as its main competitor.
It is also remarkable that AMD outperformed Intel with its business performance by a wide margin in the third quarter. The desktop shipments of Intel decreased 18% in the third quarter while its notebook shipments grew 25%, much less than the 44% shipment growth reported by AMD. This superior performance of AMD indicates that the company is gaining market share from its primary competitor at a fast pace.
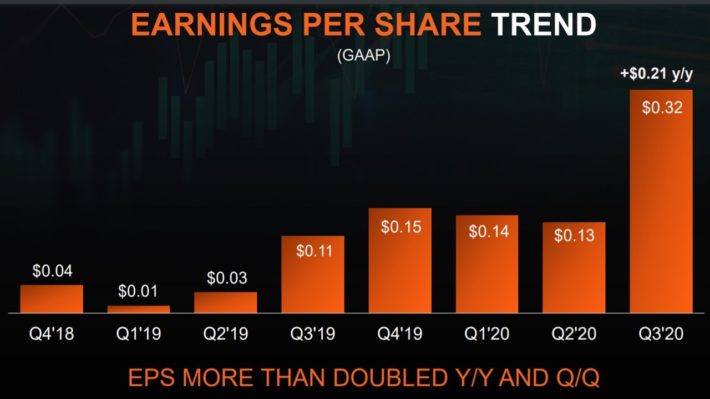
Moreover, the strong business momentum of AMD is clearly reflected in its earnings-per-share growth over last year.
Source: Investor Presentation
AMD is on track to grow its revenue 41% in the full year, achieve a gross margin of 45% and essentially double its earnings per share, from $0.64 in 2019 to $1.24 in 2020. All these metrics demonstrate the exceptionally strong business momentum of AMD.
Growth Prospects
In October, AMD announced that its upcoming Ryzen desktop processors will be the first to feature its newest Zen 3 core. This core delivers a 19% increase in Instructions Per Clock when compared to Zen 2. As a result, Ryzen 5000 desktop processors offer superior performance in gaming and productivity and thus they will be a major growth driver in the upcoming quarters.
Moreover, AMD is likely to keep growing its revenues and its earnings thanks to its technological advances and the essential duopoly status in its business. The company has more than doubled its revenues over the last five years and has switched from a loss of -$0.60 per share in 2016 to an expected profit of $1.24 per share in 2020. Analysts seem to have strong conviction in the growth trajectory of AMD, as they expect the company to double its earnings per share over the next three years.
Competitive Advantages
AMD essentially operates in a duopoly and thus it has a dominant position in its business. This position is enhanced by the growing scale of the company. As a result, AMD has a meaningful competitive advantage.
On the other hand, investors should always keep in mind that the tech sector is characterized by high uncertainty due to the fierce technological competition among its players. Less than five years ago, AMD was struggling to become profitable.
Fortunately, it has managed to create a sustainable growth trajectory in the last few years thanks to its technological achievements, which have rendered the products of the company vital components of the computer industry. However, in the tech sector, the risk of obsolescence due to the achievements of competitors is always present, particularly for investors with a long-term investing horizon.
Some tech stocks cannot pay dividends to their shareholders due to their lack of earnings. Uber (UBER) and Lyft (LYFT) have not managed to become profitable yet while Netflix (NFLX) has not managed to generate positive free cash flows yet. This is not the case for AMD, which has posted profits in the last three years and positive free cash flows in the last two years.
Will AMD Ever Pay A Dividend?
The primary reason behind the absence of a dividend is its high growth, which makes it much more profitable to invest cash flow back in the business instead of distributing them to the shareholders.
As AMD seems to have many years of double-digit earnings growth ahead, it is not likely to initiate a dividend anytime soon. Instead, it is likely to remain focused on its growth initiatives. Shareholders of AMD presumably are completely satisfied as long as the company keeps growing at a fast pace, without initiating a dividend.
Moreover, AMD incurred material losses in every single year between 2012 and 2017. This indicates the intense competitiveness in the tech sector, which is characterized by cut-throat competition most of the time.
High-growth companies do not offer a dividend for another reason as well. Their stocks usually enjoy such a rich valuation that a dividend is meaningless for the shareholders. To provide a perspective, AMD is currently trading at a price-to-earnings ratio of 69. Therefore, even if the company distributes 30% of its earnings in the form of dividends, it will offer just a 0.4% dividend yield.
Final Thoughts
AMD has become a high-growth tech stock in the last three years, with accelerated growth this year thanks to its high-quality processors. Thanks to the expected launch of its new processor, AMD has exciting growth prospects ahead. However, it is much more profitable to invest its earnings in its business than to distribute them in the form of dividends. The company also needs to invest heavily in its business in order to remain competitive and defend its market share. As a result, investors should not expect a dividend from AMD for the next several years.